Web3, is often defined as the future or of the internet, it represents a radical shift from traditional Web2 models, bringing decentralization and a level of autonomy to users like never before. This post aims to delve into the different layers of Web3 systems and their potential impact on businesses, especially focusing on how data management and sharing are set to transform with the introduction of decentralized systems.
Traditional Web2 Systems and Their Limitations
Before we can fully grasp the potential of Web3, it’s crucial to understand the current limitations of the Web2.0 models. In today’s interconnected business landscape, data is undeniably a company’s most vital asset. Companies usually manage their data effectively using in-house cloud or on-premise storage systems. However, the complexity increases significantly when they need to collaborate in shared environments like supply chains.
This need for data sharing often compels companies towards expensive third-party systems. In doing so, they move critical data into centralized systems outside their direct control. This results not only in a dependency on these external providers but also a vendor lock-in, creating a challenging and potentially risky situation.
This arrangement comes with potential issues. Firstly, the company becomes bound to the security measures, data handling practices, and the robustness of the third-party provider’s infrastructure. This dependency can have severe consequences if the provider encounters technical problems, security breaches, or even goes out of business.
Moreover, the structure of centralized data transfer systems often results in co-location of data, meaning data from different companies is stored in the same environment. This arrangement can lead to a scenario where a company’s confidential data resides on the same servers as its competitors’ data.
This co-location poses two main issues. Firstly, there’s an elevated risk of data leakage or contamination. If the third-party provider’s systems aren’t perfectly segregated, even a minor misconfiguration could expose sensitive data. Secondly, it raises issues of trust and integrity. The mere knowledge that one’s data is stored so close to a competitor’s can be disconcerting, causing unease and potentially damaging business relationships, particularly if the shared data involves intellectual property or other strategic assets.
Beyond these issues, the question of data ownership in a shared environment can create confusion and can potentially lead to misuse or abuse of data. The scalability of centralized systems becomes increasingly challenging and expensive as more companies join the system and add more data. In addition, ensuring regulatory compliance becomes a significant concern when sharing sensitive data across industries like healthcare or finance.
Looking towards the future, it’s clear that the importance and prevalence of data sharing within supply chains and collaborative environments will only grow. In this emerging landscape, data is no longer just a byproduct of business operations, but a valuable asset that can drive growth and competitive advantage. As such, ensuring the security, privacy, and integrity of this data is paramount.
In this context, while Web2.0 models have facilitated a degree of data sharing and collaboration, they come with significant limitations and risks. Security vulnerabilities, data privacy concerns, vendor dependence, trust issues, and regulatory compliance are just a few of the challenges companies face in today’s data-centric world. Furthermore, the centralized nature of these models can limit the ability of companies to fully leverage their data assets, due to concerns about data co-location and the potential for misuse or abuse of data.
This emerging reality underscores the urgent need for a shift towards a new paradigm. The solution lies in Web3.0 – a more secure, reliable, and decentralized model for managing and sharing data. With its focus on decentralization, Web3.0 offers the potential to overcome many of the challenges associated with Web2.0. By distributing data across multiple nodes rather than concentrating it in a single location, Web3.0 can reduce the risk of data breaches, increase transparency, and foster a greater sense of trust and integrity.
Understanding Web3 and Its Core Principles
Web3 leverages state-of-the-art technology to enable direct, peer-to-peer interactions, offering a stark contrast to the centralized Web2 models that place control in the hands of external entities. It offers a network of decentralized systems where every participant retains control over their data, a feature that holds significant implications for businesses worldwide.
This innovative Web3 framework is built upon four distinct layers: the blockchain, smart contracts, digital wallets with verifiable credentials, and artificial intelligence. Each layer plays a vital role in the functioning of the Web3 system and offers unique advantages over traditional methods.
The implementation of Web3 holds the potential to revolutionize business data management, particularly in contexts where the importance of data sharing is continuously on the rise. This innovative framework not only allows companies to navigate the complex digital landscape but also empowers them with control over their most vital asset: data.
So what are the different layers of Web3 and how do they work?
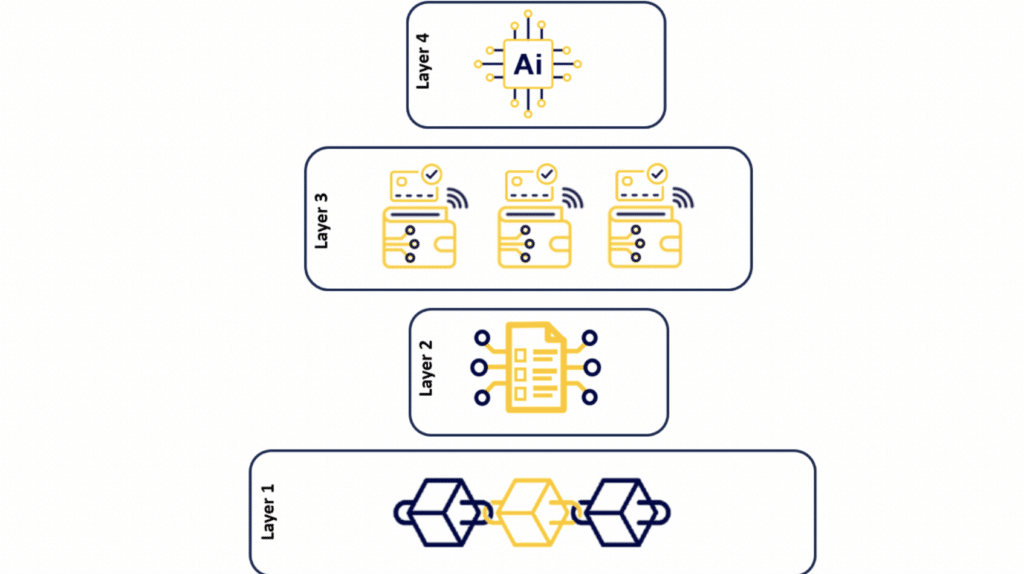
Layer 1: Digital Ledger Technology – The Bedrock of Trust, Transparency, and Data Integrity
At the heart of the Web3 framework lies digital ledger technology, providing a robust foundation for trust and transparency. Serving as a digital ledger or notary, it records hashes of events in an unalterable and transparent manner, forming the backbone of decentralized systems.
Each event or transaction in a Web3 system generates a unique digital signature, known as a hash. A hash is a fixed-length string of characters, produced by a hash function using the details of the event or transaction as input. What makes hashes exceptionally powerful is their sensitivity to input – even a minute change in the original data will result in a drastically different hash, akin to a digital fingerprint.
For example, consider a supply chain transaction where a business sells 100 units of a product to a customer. This transaction will generate a unique hash. If the quantity changes to 101 units, it will yield a completely different hash. Thus, any change in the transaction details becomes immediately evident by comparing the hash values.
Digital Ledger Technology takes the immutability of hashes a step further by providing a secure, transparent, and permanent record of these hashes. Each time a transaction occurs, a new ‘block’ containing the details of the transaction (stored as a hash) is added to the digital ledger. This sequential adding of blocks forms a chain, hence the term ‘blockchain’.
Crucially, once a block is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or erased, thanks to the use of cryptographic techniques. This immutability provides assurance that the records of transactions, the hashes, remain untouched and permanently available for verification.
The combination of hashes and Digital Ledger Technology enables companies to prove data existence, data possession, and data integrity in a Web3 system. At any point, a company can demonstrate that a specific event occurred, that they have possession of certain data, or that the data has not been altered since it was recorded, by simply showing the relevant hash and its presence on the blockchain.
In an era where data authenticity is paramount, this attribute of blockchain becomes invaluable. Whether it’s a financial transaction, a change in ownership of a digital asset, or the recording of a crucial business event, the blockchain provides an indisputable record that can prevent fraud or manipulation and resolve disputes.
For instance, in a contentious situation where a customer claims they ordered 200 units of a product but the business asserts that only 100 units were ordered, the blockchain can serve as the definitive arbitrator. By checking the hash of the transaction on the blockchain, the true details of the order can be revealed, resolving the dispute.
Layer 2: Smart Contracts – Programming Trust into Transactions
Smart contracts are an integral component in ensuring efficient, automated transactions in a decentralized environment. These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement, conditions, rules, and definitions directly written into lines of code. But they serve a purpose far beyond just automated execution of agreements. They become the vessel for embedding collective consensus and rules decided upon by the parties involved in a data supply chain, thus playing a crucial role in governing interactions within the network.
In any data supply chain, whether it involves businesses, government entities, or individuals, certain rules, definitions, and calculations are mutually agreed upon for efficient and seamless operations. For instance, in a supply chain involving the production and delivery of goods, parties would agree on definitions such as ‘order placement’, ‘delivery confirmation’, ‘payment terms’; rules such as ‘order cancellations’ or ‘returns policy’; and calculations like ‘cost estimations’ or ‘delivery time predictions’.
In a traditional setup, these agreed terms are documented, often in legal contracts or business agreements, and their enforcement depends on manual oversight or trust in the collaborating parties. This method could lead to misunderstandings, disputes, and inefficiencies due to human error.
Smart contracts in a Web3 system solve this issue. These programmable contracts can encapsulate all the collectively agreed-upon rules, definitions, and calculations directly into their code. The terms, once coded into a smart contract, are transparent, immutable, and automatically self-executing.
In a Web3 system, smart contracts work hand in hand with the blockchain, adding a layer of intelligence and consensus validation. These contracts manage the rules and definitions that guide the exchange of data, enforcing them when conditions are met. They are essential to ensuring the sanctity of data, thereby promoting trust and confidence amongst all parties involved.
Layer 3: Digital Wallets and Verifiable Credentials – Enhancing Security and Identity
Digital wallets, also known as crypto wallets, play a vital role in Web3 systems. They’re not just a ‘storage unit’ for cryptocurrencies but have a broader function in the decentralized digital environment of Web3. These wallets are designed to manage and secure an individual’s or company’s digital assets securely.
Working hand-in-hand with wallets, verifiable credentials act much like digital ID cards. They confirm your identity or other attributes, such as age or membership status, in the digital world. Stored securely in the wallet, they can be used whenever you need to prove who you are or validate certain information about you or your company online.
In a Web3 ecosystem, these wallets form the cornerstone of identity management. Each wallet contains a pair of cryptographic keys: a private key, kept secret, and a public key, shared openly. These keys work as digital signatures, authenticating the identity of a wallet’s owner.
For instance, when a user or a company wants to verify their identity, they can sign a message or a transaction with their private key. Others in the network can then use the corresponding public key to confirm that the signature is valid and the message or transaction genuinely originated from the owner of the wallet.
One powerful application of wallets in a Web3 system is in access control. With verifiable credentials, wallets can manage permissions and grant role-based access to data. For example, a company storing data on a Web3 network could use digital wallets and verifiable credentials to establish a robust access control system. Employees or partner companies can receive verifiable credentials that match their role or level of partnership. Stored in their wallets, these credentials provide access to specific data or allow certain transactions on the network.
Wallets in a Web3 system facilitate better data ownership. Unlike the conventional web setup (Web2) where user data is owned and controlled by service providers, Web3 shifts the ownership of data to the users. Each piece of data can be tied to a wallet, signifying the ownership of the data by the wallet’s owner.
Furthermore, each time data is shared or a transaction is made, it can be signed using the wallet’s private key. This signature acts as a ‘stamp of approval’ from the data owner, ensuring that the data hasn’t been tampered with and truly originates from the claimed owner. This practice adds an additional layer of trust and security to data transactions on the network.
Notably, wallets and verifiable credentials can also facilitate secure peer-to-peer connections, enabling the direct sharing of data from one system to another within the Web3 environment. This function contributes to the overall security and efficiency of data management in the emerging digital landscape.
Layer 4: Artificial Intelligence – Bringing Automation and Checks
In the layered architecture of Web3 systems, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the icing on the cake, seamlessly integrating with the foundational layers of blockchain, smart contracts, and digital wallets to enable more sophisticated operations. The intersection of AI with the Web3 paradigm facilitates an array of advanced functionalities that enhance the efficiency and security of the data sharing ecosystem. The pivotal roles that AI performs in this context are in the realms of data validation and intelligent access control.
Web3 ecosystems thrive on the quality and integrity of the data they house. Given the decentralized and peer-to-peer nature of these systems, it is vital that shared data is accurate, consistent, and trustworthy. This is where AI comes into play, acting as a tireless guardian of data integrity.
Using machine learning algorithms and statistical techniques, AI can quickly sift through vast amounts of data, scanning for inaccuracies, inconsistencies, or anomalies. This process, often referred to as data validation, is performed in real-time, ensuring that erroneous or misleading data is promptly rectified or flagged.
For example, in a decentralized healthcare data network, various entities such as hospitals, clinics, research institutions, and pharmaceutical companies share and consume data. Here, the integrity of the data is paramount as it can directly impact patient care or medical research. An AI system integrated within this network can continuously monitor the data being shared, validating it for correctness, completeness, and coherence. It can identify any anomalies or errors, such as mismatched patient records or inconsistent medical histories, and alert the concerned entities, thereby ensuring the reliability of the shared data. This automatic and real-time validation substantially enhances the quality and trustworthiness of the data in the Web3 system, driving better outcomes and insights.
In the realm of data sharing, ensuring secure and appropriate access to shared data is of utmost importance. While digital wallets with verifiable credentials play a significant role in managing access in a Web3 system, AI brings an additional layer of intelligence and proactivity to this process.
By analyzing historical access patterns and learning from past behaviors, AI can build a comprehensive understanding of typical access patterns. This knowledge allows AI to detect any unusual or potentially unauthorized access attempts, thus reinforcing the security of the data sharing process.
Consider a decentralized financial data network where banks, financial institutions, and fintech startups share sensitive financial data. In such a network, access control is critical to maintain data privacy and regulatory compliance. An AI system can monitor the access patterns in this network and detect any abnormal behavior, such as an unusual number of access requests from a particular wallet, access attempts at odd hours, or requests for data that a wallet typically doesn’t access. Upon detecting such anomalies, the AI system can either alert the network administrators or take pre-determined actions like temporarily suspending access, thereby mitigating potential data breaches.
The Future of Business Data Management with Web3 Systems
Given the four-layered structure, the adoption of Web3 systems can bring about a paradigm shift in business data management. Companies will no longer need to surrender control of their data to a third-party system, nor worry about potential breaches in data security. Web3 systems, with their
decentralized approach, provide businesses with a secure, efficient, and more autonomous model for data sharing and storage.
This shift towards decentralized systems is not just a technological transformation. It signifies a move towards a more democratized digital world, where control over data is given back to the individuals or entities that own them.
However, the journey towards this decentralized future is not without challenges. Issues of scalability, interoperability between different blockchains, regulatory compliance, and the technological learning curve need to be tackled. Nevertheless, the potential benefits that Web3 systems offer make them worth the effort.
The age of Web3 is here, promising opportunities and possibilities that could revolutionize our digital world. As technological leaders, we must not just adapt to these changes but should be the ones leading this digital transformation. We are in an exciting era of technological evolution, and I am eager to witness the transformations Web3 systems will bring to the world of data management. The journey towards a decentralized and democratic digital future is only just beginning. Let’s embrace it, navigate through its challenges, and utilize it to its full potential for the betterment of our digital world.